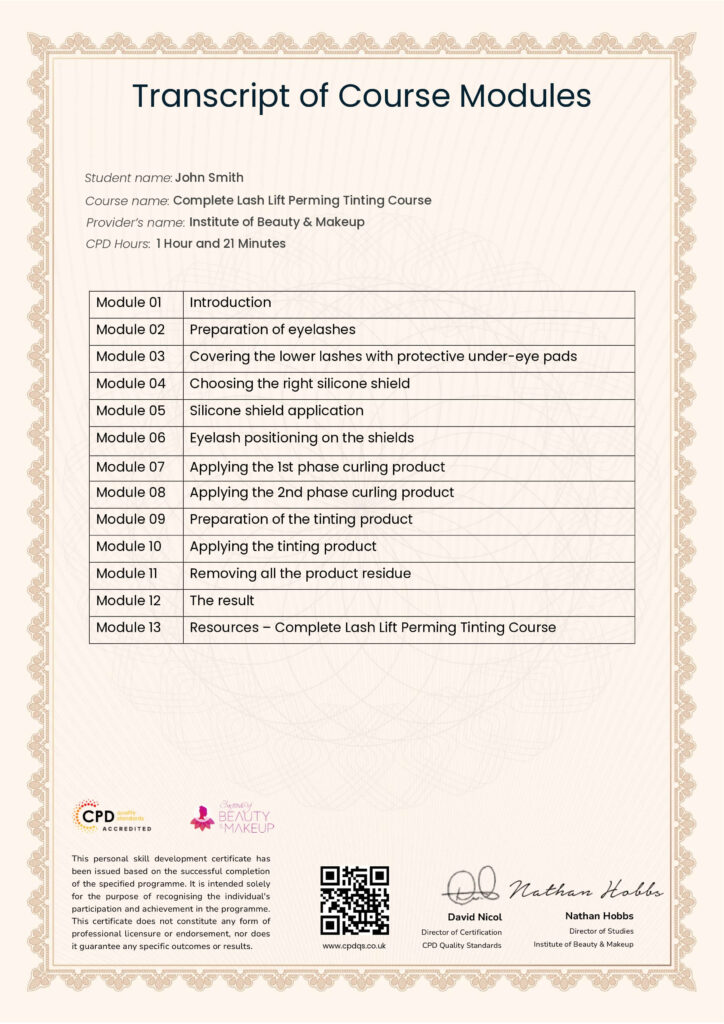
-
Login
-
Sign Up

Log in to your iBeauty account
Access Your Account for a Universe of Possibilities
at Your Fingertips.

Sign up and start learning
Take the First Step Towards Learning. Sign Up Today &
Expand Your Horizons!
Log In
Sign Up
Don’t have an account yet? Sign Up
or continue with
By Sign up, you agree to our Terms and Use and Privacy Policy
Already have an account? Sign In
Electric Circuits for Electrical Engineering
0
Course overview Learn about Trainee Train Driver quickly and enhance your skills. You will understand Trainee Train Driver and its …
Related Courses
Level 7 QLS Endorsed | 24/7 Student Support | 20% OFF Certificate & Transcript
Level 7 QLS Endorsed | 24/7 Student Support | 20% OFF Certificate & Transcript
Level 3 QLS Endorsed | 24/7 Student Support | 20% OFF Certificate & Transcript
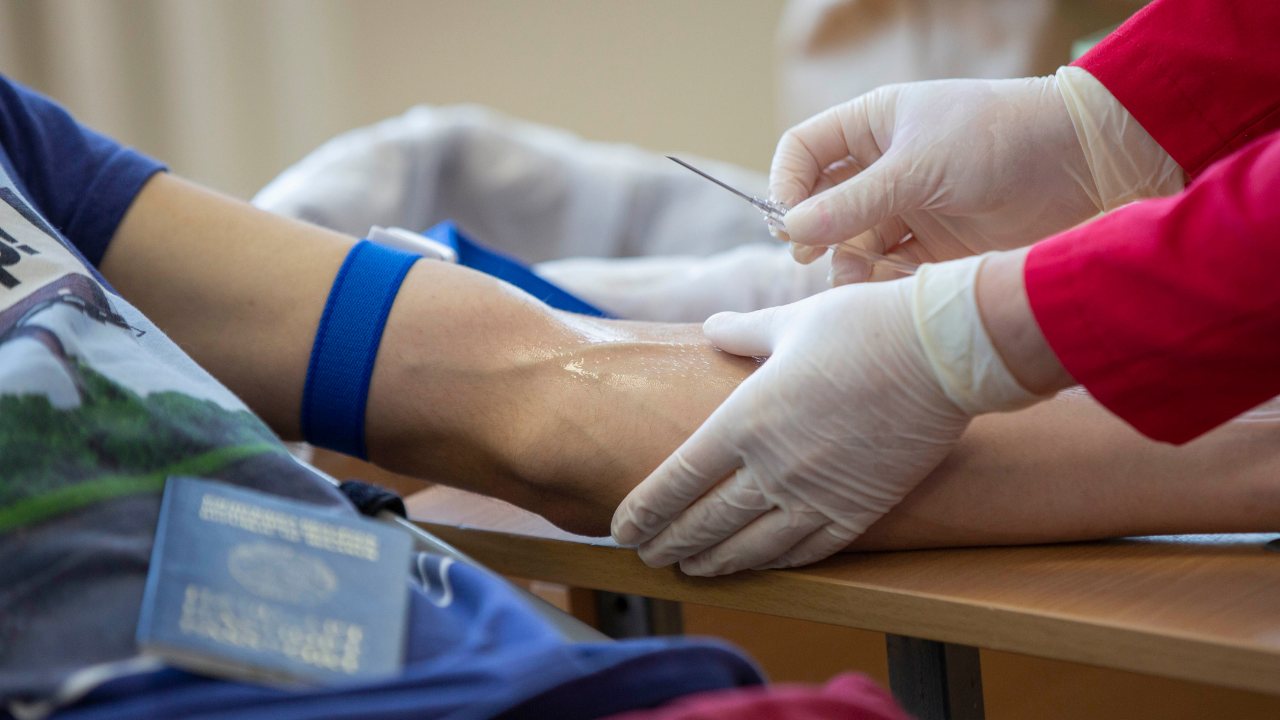
This Phlebotomy course has been broken down into several user-friendly modules, taught by an experienced professional who will take you through each topic step-by-step.